Blood glucose in diabetes is managed through effective monitoring using tools like glucose meters and continuous glucose monitors, along with a balanced diet and understanding the role of insulin.
Blood glucose in diabetes plays a pivotal role in how individuals manage their condition. If you’ve ever wondered how this affects your health, stick around as we unravel the connections between glucose levels and diabetes management.
What is blood glucose and why is it important?
Blood glucose refers to the amount of sugar, or glucose, present in your blood. This is an essential source of energy for your body’s cells. Maintaining a healthy blood glucose level is crucial, especially for those with diabetes, where the body cannot effectively manage glucose levels. Understanding how blood glucose works helps individuals make informed choices about their diet and lifestyle.
How Blood Glucose Works
When we eat, our body breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, which then enters the bloodstream. The pancreas produces insulin, a hormone that helps cells absorb glucose for energy or storage. If insulin levels are inadequate, as in diabetes, glucose remains in the bloodstream, leading to high blood sugar levels.
Importance of Regular Monitoring
For people with diabetes, regular monitoring of blood glucose levels can prevent complications such as heart disease and nerve damage. Keeping track of these levels allows for timely adjustments in diet, medication, or activity levels, promoting better overall health.
Effects of High and Low Blood Glucose
High blood glucose, or hyperglycemia, can result in symptoms like frequent urination, increased thirst, and fatigue. Over time, it can lead to serious health issues, including kidney damage and vision problems. Conversely, low blood glucose, known as hypoglycemia, can cause dizziness, confusion, and even loss of consciousness, representing a medical emergency.
Making Informed Choices
By understanding blood glucose and its impact, individuals can make informed choices to maintain their health. Choosing balanced meals, engaging in regular physical activity, and following medical advice can significantly aid in blood sugar management.
Understanding normal and abnormal glucose levels

Understanding normal and abnormal glucose levels is crucial for managing diabetes effectively. Blood glucose levels fluctuate throughout the day based on various factors, including diet, activity, and overall health. Knowing what these levels mean helps in making informed health decisions.
Normal Glucose Levels
For most individuals, normal fasting blood glucose levels range from 70 to 100 mg/dL. After eating, glucose levels can rise, but should generally not exceed 140 mg/dL.
Abnormal Glucose Levels
When blood glucose levels exceed the normal range, it can lead to several conditions. Hyperglycemia occurs when blood glucose levels are too high, typically above 130 mg/dL when fasting or 180 mg/dL after meals. This can be a sign of uncontrolled diabetes and requires immediate attention.
Symptoms of High Glucose Levels
High glucose levels may cause symptoms such as increased thirst, frequent urination, and fatigue. Recognizing these signs early can help prevent serious complications.
Low Glucose Levels
On the other hand, hypoglycemia occurs when blood glucose levels drop below 70 mg/dL. This can lead to dizziness, confusion, and even fainting. It is important for individuals managing diabetes to understand how to prevent and treat low blood sugar cases.
Regular Monitoring
Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels is essential. Using a glucose meter, individuals can track their levels and adjust their diet and medication accordingly. This practice enables better management of their condition.
The role of diet in managing blood glucose
The role of diet in managing blood glucose is essential for people with diabetes. Eating the right foods can help maintain a stable blood sugar level. Understanding which foods to choose can make a significant difference in health outcomes.
Balanced Nutrition
A balanced diet includes a mix of carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats. Complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains and legumes, are preferred over simple carbohydrates found in sugary snacks. These foods break down slowly, helping to keep blood sugar levels stable.
Fiber-Rich Foods
Incorporating fiber-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can improve blood glucose control. Fiber slows the absorption of sugar, protecting against spikes in blood sugar after meals.
Healthy Fats and Protein
Including healthy fats, such as those from avocados, nuts, and olive oil, can also support blood glucose management. Proteins, especially those from lean sources like chicken, fish, and beans, play a crucial role in feeling full and stable throughout the day.
The Importance of Portion Control
Portion control is vital. Eating too much, even healthy foods, can lead to increased blood sugar levels. Using smaller plates, checking serving sizes, and being mindful can help maintain appropriate portions.
Monitoring and Adjusting Diet
Regularly monitoring blood glucose levels allows individuals to see how different foods affect their sugar levels. Using this information to adjust their diet can lead to better management of their diabetes.
Insulin and its impact on blood glucose
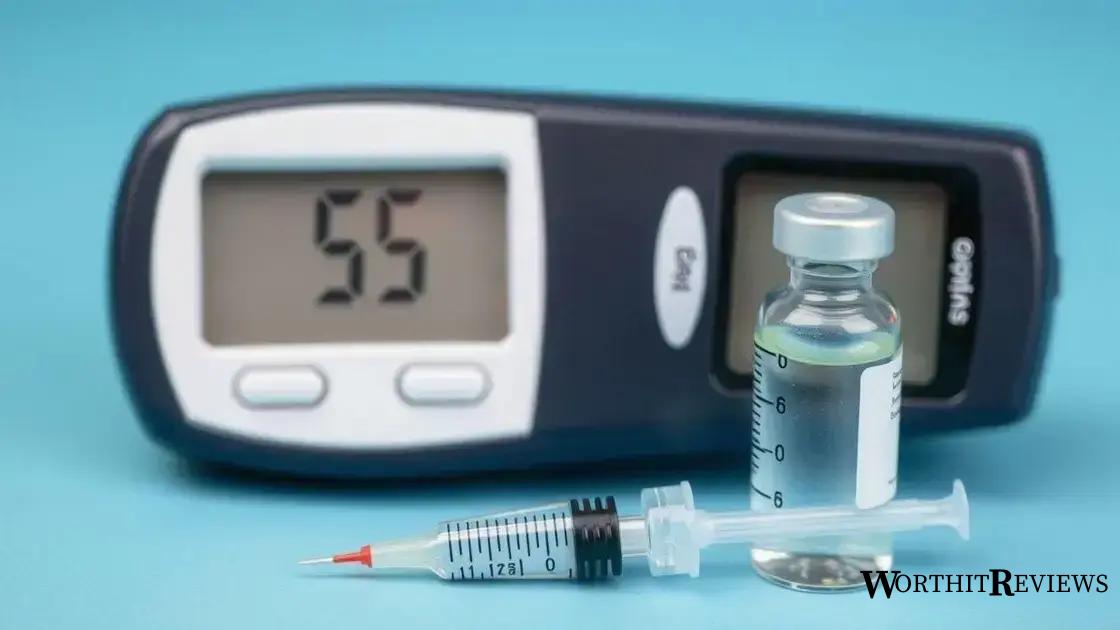
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that plays a vital role in regulating blood glucose levels. It helps cells in the body absorb glucose for energy or store it for later use. Understanding how insulin functions can help individuals manage their blood sugar effectively.
The Function of Insulin
When you eat, your blood glucose levels rise. In response, the pancreas releases insulin into the bloodstream. Insulin helps transport glucose from the blood into the cells, decreasing blood sugar levels. This process is essential for maintaining energy levels and overall health.
Types of Diabetes and Insulin
There are different types of diabetes, each affecting insulin production and its effectiveness. In Type 1 diabetes, the body does not produce insulin at all. In Type 2 diabetes, the body becomes resistant to insulin, making it less effective. Understanding these types can guide treatment options.
Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance occurs when cells in the body do not respond effectively to insulin. This condition leads to higher blood glucose levels and can be managed through lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise, or medication as needed.
Importance of Insulin Therapy
For those with Type 1 diabetes or advanced Type 2 diabetes, insulin therapy is essential. This involves regular insulin injections or the use of an insulin pump to help manage blood sugar levels effectively.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Regularly monitoring blood glucose levels allows individuals to see how their body responds to insulin. This helps in making necessary adjustments to diet, activity, and medication to maintain balanced sugar levels.
Tools for monitoring blood glucose effectively
Monitoring blood glucose effectively is essential for managing diabetes. There are several tools available that can help individuals keep track of their blood sugar levels.
Blood Glucose Meters
Blood glucose meters are the most common devices used for monitoring diabetes. These portable devices measure blood sugar levels by requiring a small drop of blood, usually obtained from a fingertip. Users can see their results quickly and record them for future reference.
Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGM)
Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) provide real-time glucose readings throughout the day and night. These devices are worn on the body and automatically track blood sugar levels, sending data to a smartphone or a receiver. This continuous monitoring allows individuals to see trends and make timely adjustments in their diet or medication.
Smartphone Apps
Many smartphone apps are available that can help individuals log their blood glucose readings, food intake, and insulin doses. These apps may offer reminders and graphs to visualize trends in blood sugar levels, making it easier to manage diabetes.
Insulin Pumps
Some people use insulin pumps, which deliver a continuous supply of insulin based on current blood sugar levels. Many modern insulin pumps are compatible with CGMs, making blood glucose management more seamless and efficient.
Regular Consultations
Regular consultations with healthcare providers are essential for optimal blood glucose management. Healthcare professionals can recommend appropriate tools and help interpret data from blood glucose monitoring to enhance overall diabetes management.
Wrapping Up: Managing Blood Glucose in Diabetes
Managing blood glucose levels is crucial for those living with diabetes. With the right tools, such as glucose meters and continuous glucose monitors, individuals can effectively track their sugar levels and make informed decisions.
Diet plays a significant role in blood sugar management. Choosing balanced meals with the right carbs, proteins, and fats can keep glucose levels stable.
Understanding the impacts of insulin and ensuring regular monitoring can aid in maintaining overall health. With supportive tools and knowledge, managing diabetes becomes much more manageable.
Taking charge of your health means being proactive and aware of how lifestyle choices affect blood glucose and overall well-being.
