Managing blood glucose levels in type 2 diabetes requires a combination of dietary choices, regular exercise, medication, and effective stress management to prevent serious long-term health complications.
Blood glucose type 2 diabetes plays a crucial role in health and well-being. You might wonder, how can one manage their levels to lead a better life? Let’s dive into practical tips and insights.
Understanding blood glucose in type 2 diabetes
Understanding blood glucose levels is crucial for managing type 2 diabetes. Blood glucose, also known as blood sugar, is the main type of sugar found in the blood and is the body’s primary source of energy.
In people with type 2 diabetes, the body either resists the effects of insulin—a hormone that helps glucose enter cells—or doesn’t produce enough insulin to maintain normal glucose levels. As a result, blood glucose levels can become elevated, leading to various health complications.
Normal vs. Elevated Blood Glucose Levels
Normal fasting blood glucose levels typically range from 70 to 99 mg/dL. When levels rise above 126 mg/dL after fasting, it may indicate diabetes. Regular monitoring can help catch these changes early.
The Role of Insulin
Insulin is essential for regulating blood sugar. It allows glucose to enter the cells where it can be used for energy. When the body can’t use insulin properly, blood sugar levels remain high, which can lead to serious health issues.
Effects of High Blood Glucose
Consistently high blood glucose can cause symptoms like excessive thirst, frequent urination, and fatigue. Over time, it may result in complications such as nerve damage, kidney problems, and heart disease. Therefore, understanding how to manage these levels is vital for health.
Managing Blood Glucose Levels
Managing blood glucose involves a combination of dietary choices, physical activity, and, in some cases, medication. Incorporating whole grains, fruits, and vegetables into your diet can help stabilize blood sugar levels. Regular exercise can also enhance insulin sensitivity, aiding glucose control.
Symptoms and risk factors of high blood glucose

Recognizing the symptoms and risk factors of high blood glucose is essential for effective management of type 2 diabetes. Common symptoms include:
- Increased thirst: One of the first signs of high blood sugar is often feeling very thirsty.
- Frequent urination: High glucose levels make kidneys work harder, leading to more trips to the bathroom.
- Fatigue: People with elevated blood sugar may feel tired and lethargic because their bodies are not using glucose effectively.
- Blurred vision: High blood sugar can lead to changes in vision as the lenses of the eyes lose their ability to focus.
- Slow-healing wounds: Elevated glucose levels can impair the body’s ability to heal properly.
Understanding these symptoms is vital for early intervention. If you notice any of these signs, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional.
Risk Factors for High Blood Glucose
Several risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing high blood glucose:
- Obesity: Excess body weight is a significant risk factor for type 2 diabetes, often leading to insulin resistance.
- Sedentary lifestyle: Lack of physical activity can contribute to weight gain and higher blood sugar levels.
- Age: The risk increases with age, especially after 45 years.
- Family history: A family history of diabetes raises your likelihood of developing the condition.
- High blood pressure: Having high blood pressure can increase the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Being aware of these symptoms and risk factors can empower individuals to take proactive steps to manage their health.
Dietary choices to manage blood glucose
Making the right dietary choices is essential for managing blood glucose levels in individuals with type 2 diabetes. A balanced diet can help maintain stable blood sugar levels and improve overall health.
Here are some key components to consider:
Choose Whole Grains
Whole grains are an excellent source of fiber, which can help control blood sugar levels. Foods like brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread break down slowly, leading to gradual increases in blood sugar.
Incorporate Plenty of Vegetables
Vegetables are low in calories and high in nutrients. Aim to fill half your plate with non-starchy vegetables, such as spinach, broccoli, and bell peppers. These foods are high in fiber and can aid digestion.
Include Lean Proteins
Incorporating lean proteins, like chicken, turkey, tofu, and legumes, can help keep you full and stabilize blood sugar. Protein has little effect on blood glucose, making it a smart choice for managing diabetes.
Limit Sugary Foods and Beverages
Foods high in added sugars can cause spikes in blood glucose. Limit sugary drinks, snacks, and desserts. Instead, opt for natural sugars found in fruits, which also contain fiber.
Watch Portion Sizes
Portion control is vital. Even healthy foods can cause blood sugar spikes if eaten in large quantities. Use smaller plates and be mindful of serving sizes to help maintain balance.
Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water can help keep you hydrated and support your body’s overall function. Avoid sugary drinks that can raise blood sugar levels.
By making these dietary choices, individuals with type 2 diabetes can better manage their blood glucose levels and support their long-term health.
Exercise and its impact on blood glucose levels

Exercise plays a vital role in managing blood glucose levels for individuals with type 2 diabetes. Regular physical activity can help maintain a healthy weight and lower blood sugar.
Engaging in exercise helps your body use insulin more effectively. This can lead to improved blood sugar control over time. There are several ways exercise impacts blood glucose:
Improved Insulin Sensitivity
Regular physical activity increases insulin sensitivity. This means your cells can use available insulin more effectively. As a result, blood glucose levels can decrease after exercise.
Lowering Blood Sugar Levels
During exercise, muscles use sugar for energy, which can lower blood sugar levels. This is especially beneficial for people who may experience spikes in glucose due to food consumption.
Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for managing diabetes. Exercise helps burn calories and builds muscle mass, which can aid in weight loss. Even a small amount of weight loss can have a positive effect on blood sugar control.
Types of Exercise
Incorporating aerobic activities such as walking, cycling, or swimming into your routine can effectively lower blood glucose. Additionally, strength training helps build muscle and can improve overall metabolism.
Consistency is Key
For optimum effects on blood sugar, consistency is essential. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity each week, alongside strength training two days a week.
Before starting any exercise program, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider, especially for those with diabetes, to tailor activities to individual health needs.
How stress affects blood sugar
Stress has a significant impact on blood sugar levels, especially in individuals with type 2 diabetes. When you experience stress, your body releases hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline. These hormones can cause blood sugar levels to rise.
Understanding how stress affects your body can help you manage your blood sugar more effectively. Here are some key points:
Hormonal Response
During stressful situations, the body enters a “fight or flight” mode. This response prepares you to react quickly, but it also leads to increased blood sugar levels as the body releases stored glucose for energy.
Impact on Insulin Sensitivity
Chronic stress can lead to insulin resistance. This means your body becomes less efficient at using insulin, making it harder to control blood sugar levels. Managing stress effectively can improve insulin sensitivity.
Emotional Eating
Many people turn to food for comfort during stressful times. This can lead to unhealthy eating habits, which may result in higher blood sugar. Being mindful of your food choices during stress is important.
Sleep Disruption
Stress can also affect your sleep quality. Poor sleep can contribute to higher blood sugar levels, creating a cycle of stress and elevated glucose that is difficult to break.
Effective Stress Management
Finding healthy ways to manage stress is crucial. Techniques such as deep breathing, mindfulness, exercise, and hobbies can help you relax and lower stress levels, benefiting your overall health. Consider incorporating these practices into your daily routine to help keep your blood sugar stable.
Monitoring blood glucose effectively
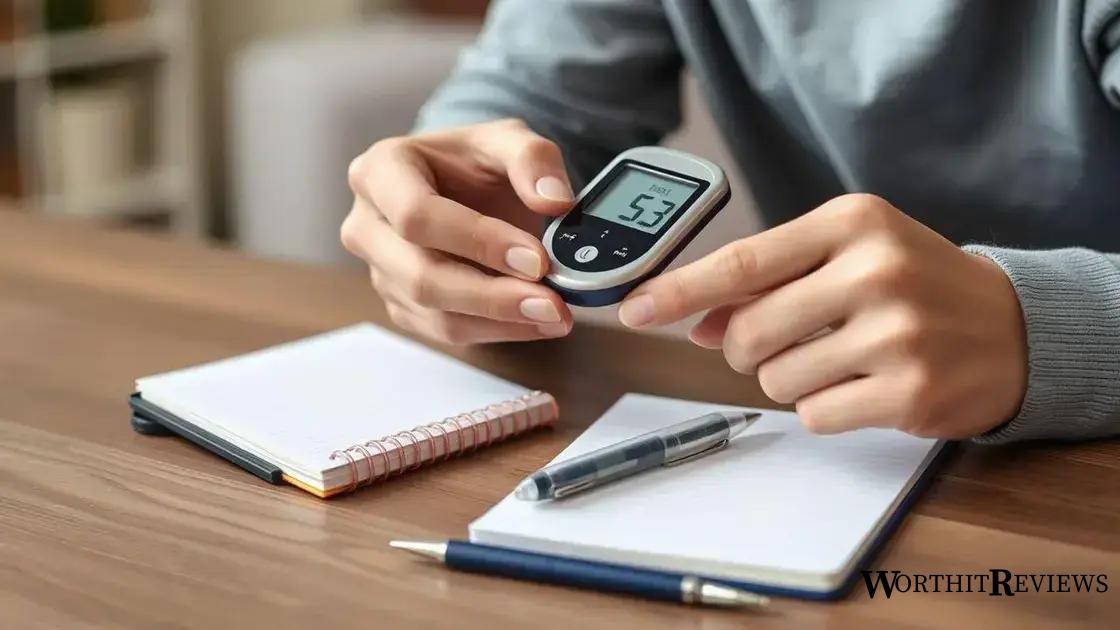

Monitoring blood glucose levels is a crucial aspect of managing type 2 diabetes. Regular checks can help you understand how your body responds to food, exercise, and medication.
Here are some key points to consider when monitoring blood glucose:
The Importance of Regular Monitoring
Keeping track of your blood glucose levels helps you identify patterns and trends. This information can be valuable for adjusting your diet, activity, and medication as needed.
How to Monitor Blood Glucose
There are different methods to monitor your blood glucose levels:
- Glucose Meters: These handheld devices require a small drop of blood to give you an immediate reading. It’s essential to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for accurate results.
- Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs): CGMs are wearable devices that continuously track blood sugar levels throughout the day and night. They provide real-time data and alerts if levels become too high or too low.
Understanding Your Target Range
Discuss with your healthcare provider about what your target blood glucose range should be. Generally, for many adults with diabetes, the fasting blood sugar goal is between 80-130 mg/dL. After meals, it may be below 180 mg/dL.
Keeping a Blood Sugar Log
Keeping a record of your blood glucose readings alongside notes about your meals, exercise, and medication can help you and your healthcare team spot trends. This log can be digital or on paper.
Reacting to Results
If your blood glucose levels are consistently outside your target range, it’s important to speak with your healthcare provider. They can help you make necessary adjustments to your management plan.
By effectively monitoring your blood glucose, you can take an active role in managing your diabetes and reducing the risk of complications.
Role of medication in blood glucose management
Medication plays a crucial role in managing blood glucose levels for many individuals with type 2 diabetes. When lifestyle changes alone are not enough to keep blood sugar levels in check, medication can offer additional support.
There are several types of medications used to help manage blood glucose:
1. Oral Medications
Oral medications are usually the first line of treatment. They work in various ways:
- Metformin: This is often the first medication prescribed. It helps lower glucose production in the liver and improves insulin sensitivity.
- Sulfonylureas: These medications stimulate the pancreas to release more insulin, helping lower blood sugar levels.
- GLP-1 receptor agonists: They work by increasing insulin secretion in response to meals and slowing gastric emptying.
2. Insulin Therapy
For some individuals, insulin therapy may be necessary. This involves administering insulin through injections or an insulin pump. It helps to directly lower blood glucose levels in the body.
3. Monitoring and Adjusting Medications
Regular monitoring of blood glucose is essential to determine the effectiveness of medication. It’s important to work with a healthcare provider to adjust medications based on blood sugar readings and individual responses.
4. Side Effects and Considerations
While medications can be effective, they may also have side effects. Common side effects include nausea, weight gain, and low blood sugar levels. Discuss these with your healthcare provider to find the best options with manageable side effects.
Taking medications as prescribed, alongside lifestyle modifications such as a healthy diet and regular exercise, can make a significant difference in managing blood sugar levels effectively.
Long-term effects of uncontrolled blood sugar
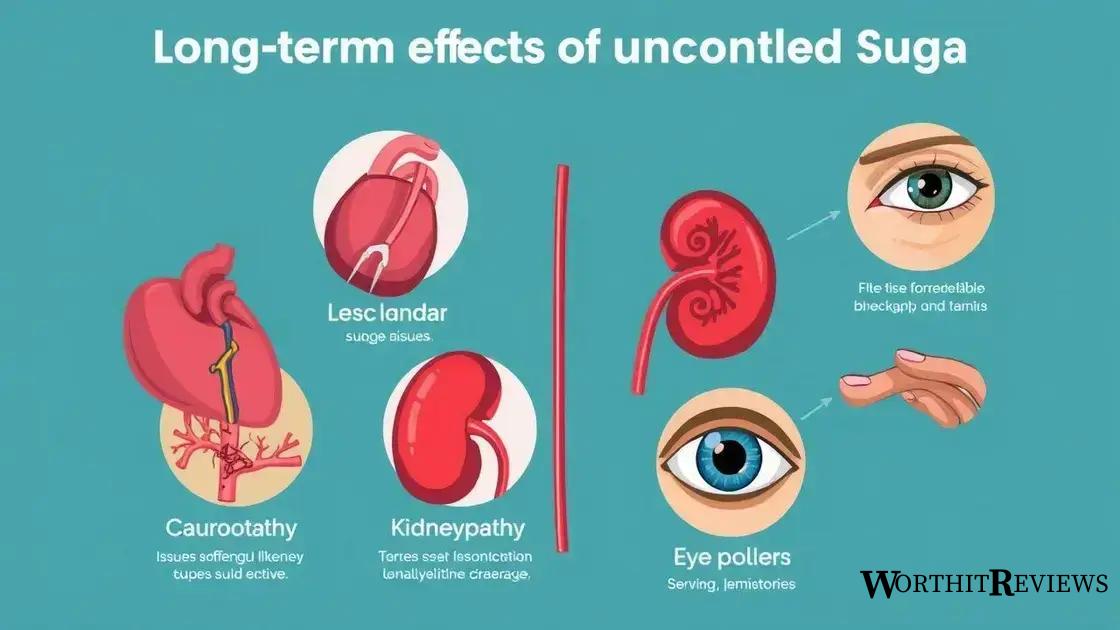
Uncontrolled blood sugar levels can lead to serious long-term effects on the body, particularly for those with type 2 diabetes. It is crucial to understand these potential complications to motivate better management of blood glucose.
1. Cardiovascular Disease
Long-term high blood sugar can damage blood vessels and nerves that control the heart. This increases the risk of heart attack and stroke. Maintaining controlled blood sugar levels helps reduce these risks.
2. Neuropathy
Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to diabetic neuropathy, a condition where high glucose levels damage nerves throughout the body. Symptoms may include numbness, tingling, and pain in the hands and feet.
3. Kidney Damage
High blood sugar can also harm the kidneys, leading to diabetic nephropathy. Over time, this can result in kidney failure, requiring dialysis or a kidney transplant. Regular monitoring and control of blood sugar can reduce this risk.
4. Eye Problems
Diabetes increases the risk of serious eye conditions, including diabetic retinopathy. This occurs when high sugar levels damage the blood vessels in the retina, potentially leading to vision loss or blindness.
5. Foot Complications
High blood sugar can reduce blood flow and damage nerves in the feet, making it harder to feel injuries. Untreated wounds can lead to infections and, in severe cases, may require amputation.
6. Skin Conditions
People with diabetes are more prone to skin infections and disorders, such as fungal infections. High blood sugar creates an environment that allows these infections to thrive.
Understanding the long-term effects of uncontrolled blood sugar emphasizes the importance of regular monitoring, medication, and lifestyle changes to maintain healthy blood glucose levels.
Managing blood glucose for better health
In summary, managing blood glucose levels is essential for those with type 2 diabetes. By understanding the effects of diet, exercise, and medication, individuals can take charge of their health.
Regular monitoring and effective stress management also play crucial roles in maintaining blood sugar levels. Recognizing the long-term risks of uncontrolled blood sugar can motivate better lifestyle choices.
By making informed decisions, making healthier choices, and staying proactive, individuals can live healthier lives and reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions About Managing Blood Glucose Levels
What is the importance of monitoring blood glucose levels?
Monitoring blood glucose levels helps individuals understand how their body responds to food, exercise, and medication, allowing for better management of diabetes.
How can diet affect blood sugar levels?
A healthy diet, rich in whole grains, lean proteins, and vegetables, can help stabilize blood sugar levels and improve overall insulin sensitivity.
What types of exercise are best for managing blood glucose?
Aerobic exercises like walking, cycling, and swimming, combined with strength training, are effective for improving insulin sensitivity and lowering blood sugar.
What role does medication play in blood glucose management?
Medication can help lower blood glucose levels when lifestyle changes are not enough. It can include oral medications or insulin therapy as prescribed by a healthcare provider.
What are the long-term effects of uncontrolled blood sugar?
Uncontrolled blood sugar can lead to serious complications such as cardiovascular diseases, neuropathy, kidney damage, and vision problems.
How can stress management impact blood sugar control?
Effective stress management techniques, like deep breathing and exercise, can reduce stress hormones that raise blood sugar, helping to maintain stable glucose levels.
