Maintaining stable blood sugar levels for individuals with type 2 diabetes involves a balanced diet, regular exercise, consistent monitoring, and effective stress management.
Blood sugar levels of type 2 diabetes can often feel like a mystery. Do you find yourself wondering how daily choices impact your blood glucose? Let’s dive into the details and uncover strategies for better management.
What influences blood sugar levels in type 2 diabetes?
Many factors can influence blood sugar levels in type 2 diabetes. Understanding these factors is crucial for effective management and overall health. One significant factor is diet. Consuming foods high in carbohydrates can cause spikes in blood sugar, while a balanced diet with fiber, protein, and healthy fats can help maintain stable levels.
Another important factor is physical activity. Regular exercise can improve insulin sensitivity, helping the body better utilize glucose from the bloodstream. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity each week.
Stress can also greatly affect blood sugar levels. When stressed, the body releases hormones like cortisol that can raise glucose levels. Finding stress-reduction techniques, such as meditation or yoga, can be beneficial.
Medications play a crucial role as well. Some medications are designed to lower blood sugar, while others may lead to increases. It’s important to work closely with a healthcare provider to find the right medication.
Finally, sleep quality should not be overlooked. Poor sleep can disrupt hormones that regulate blood sugar, leading to higher levels. Aim for 7-9 hours of good-quality sleep each night to promote better health.
Understanding the role of diet and blood sugar
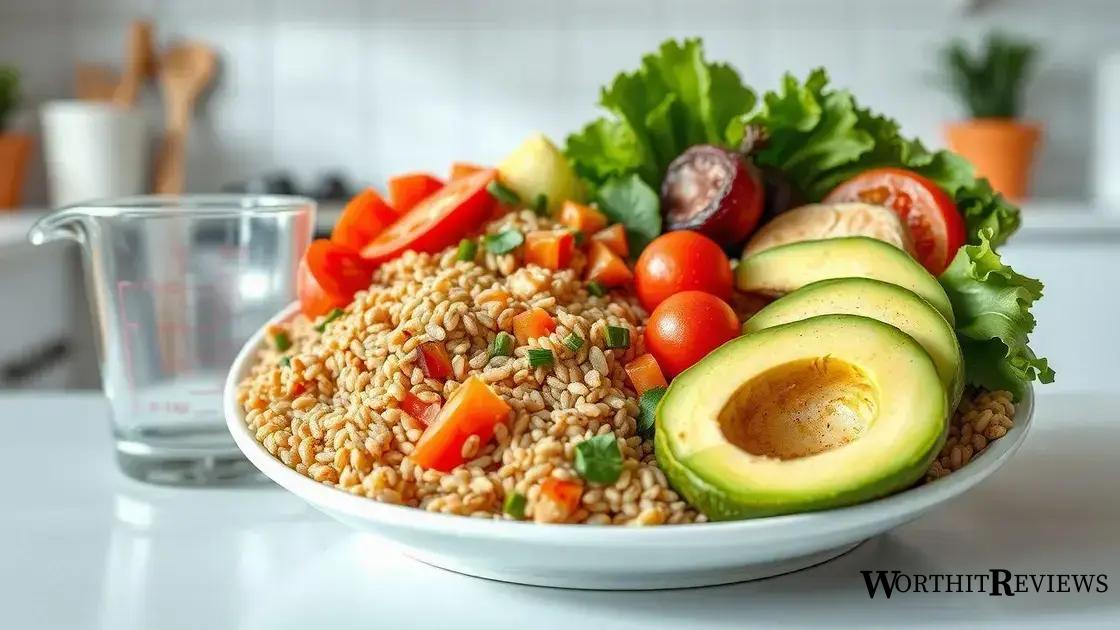

The role of diet in managing blood sugar levels, especially for those with type 2 diabetes, is crucial. What you eat can directly affect how your body processes glucose. A well-planned diet can help keep your blood sugar stable, preventing spikes and drops.
Carbohydrates are the primary source of glucose in the diet. It’s essential to understand that not all carbohydrates are equal. Foods like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables provide fiber, which slows down the absorption of sugar. This helps in maintaining more stable blood sugar levels.
Portion control is another important aspect. Eating smaller, balanced meals throughout the day can help regulate blood sugar. Large meals can lead to significant spikes in glucose levels, so it’s advisable to eat in moderation.
Healthy fats, such as those found in avocados and nuts, along with lean proteins, play a vital role as well. These foods contribute to feeling full and can prevent overeating, which helps in controlling blood sugar.
It’s also beneficial to limit foods high in sugar and refined carbs, like sugary snacks and white bread. These can cause rapid increases in blood sugar levels and lead to challenges in managing diabetes.
Exercise: a powerful tool for managing blood sugar
Engaging in regular exercise is a powerful tool for managing blood sugar levels, particularly for individuals with type 2 diabetes. Physical activity increases insulin sensitivity, which helps your body utilize glucose more effectively.
There are many types of exercise to consider. Aerobic activities, such as walking, running, cycling, and swimming, get your heart rate up and can significantly improve overall health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week.
Strength training is equally important. Lifting weights or using resistance bands can build muscle, which burns more calories and helps your body manage blood sugar better. Aim to include strength training exercises at least twice a week.
Flexibility and balance exercises are also beneficial. Activities like yoga and tai chi can enhance flexibility, reduce stress, and improve overall wellbeing, which is essential for maintaining healthy blood sugar levels.
Before starting any exercise program, it’s wise to consult with a healthcare provider, especially for those with diabetes. They can provide personalized recommendations based on individual health conditions.
The impact of stress on blood sugar levels
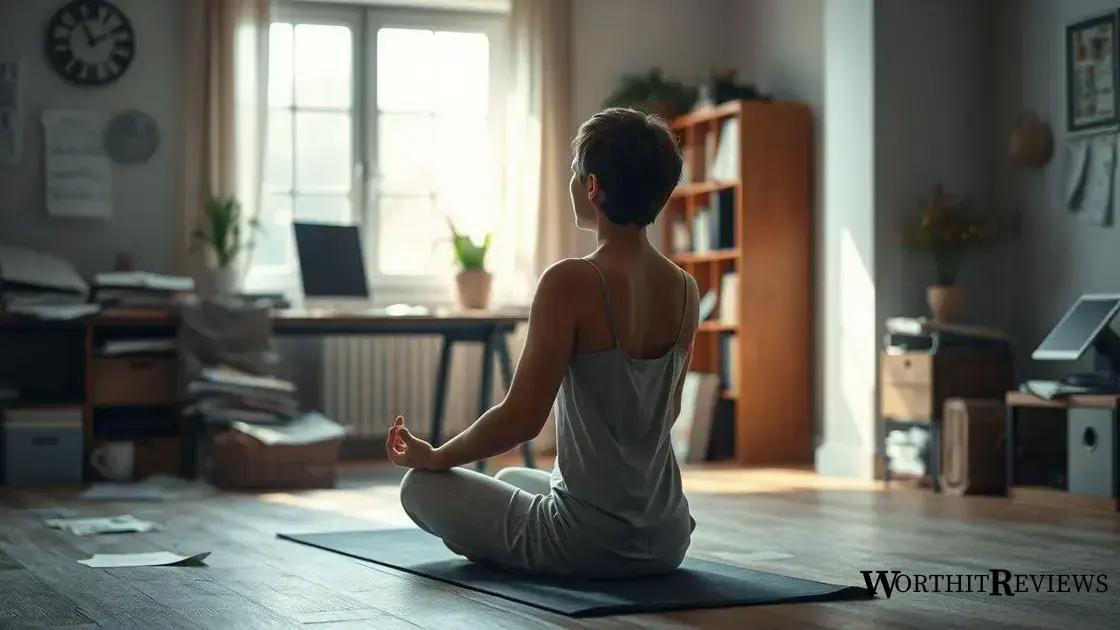

Stress can have a profound impact on blood sugar levels, especially for those managing type 2 diabetes. When you experience stress, your body releases hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline. These hormones prepare your body for “fight or flight” responses, leading to increased sugar production in the liver and higher blood glucose levels.
Chronic stress can perpetuate this cycle. When stress becomes a regular part of life, your body may produce excessive amounts of glucose, resulting in persistently elevated blood sugar levels. This can make managing diabetes more challenging.
Identifying sources of stress is crucial for effective management. Common stressors include work issues, family challenges, and financial worries. Recognizing these triggers can help you develop strategies to cope.
Incorporating relaxation techniques, such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises, can greatly reduce stress and improve your overall health. Regular physical activity also serves as a powerful stress reliever and helps burn off excess glucose.
It’s important to monitor how stress affects your blood sugar. Keeping a blood sugar log can help you notice patterns related to stress and glucose levels, allowing you to adapt your management plan accordingly.
Monitoring your blood sugar: best practices
Monitoring your blood sugar is a key aspect of managing type 2 diabetes. Keeping track of your levels can help you understand how your body responds to different foods, activities, and stressors. Here are some best practices for effective monitoring.
First, it’s important to establish a routine. Check your blood sugar at the same times each day, such as before and after meals, or before bedtime. Consistency helps create a reliable pattern, allowing you to identify what affects your blood sugar levels.
Use a glucometer that you are comfortable with. Many modern devices are user-friendly and can give quick results. Don’t hesitate to ask your healthcare provider for recommendations tailored to your needs.
Record your numbers in a logbook or an app. Include the date, time, and any relevant notes about food, exercise, and stress. This information can help you spot trends over time and facilitate discussions with your healthcare team.
Be aware of target blood sugar ranges as per your healthcare provider’s advice. Knowing when your levels are too high or too low can guide your diet and activity choices.
Lastly, maintain an open line of communication with your healthcare provider. Share your logs and any concerns you may have. Adjustments may be necessary based on your monitoring data, and working closely with your provider can ensure better outcomes.
How medications affect blood sugar levels
Medications play a vital role in managing blood sugar levels for those with type 2 diabetes. Different types of medications work in various ways to help control these levels.
Oral medications are often the first line of treatment. Metformin is one of the most commonly prescribed. It helps lower blood sugar by improving insulin sensitivity and reducing glucose production in the liver. This can lead to better blood sugar control without causing significant weight gain.
Another class of medications is sulfonylureas, which stimulate the pancreas to release more insulin. While this can lower blood sugar effectively, it may also lead to low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) if not monitored closely.
Additionally, there are GLP-1 receptor agonists that improve blood sugar control by increasing insulin secretion in response to meals, slowing gastric emptying, and reducing appetite. These can help with weight management as well.
For some patients, insulin therapy may be necessary. Insulin helps lower blood sugar by allowing cells to use glucose for energy. It’s essential to monitor blood sugar closely when on insulin, as there is a risk of low levels.
Always consult with a healthcare provider about how medications affect your individual blood sugar. Different medications may work better for different people. Regular check-ups and adjustments may be necessary to find the best treatment plan.
Tips for maintaining stable blood sugar levels
Maintaining stable blood sugar levels is vital for overall health, especially for those with type 2 diabetes. Here are some practical tips to help you achieve this.
1. Follow a balanced diet: Focus on a diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, and plenty of fruits and vegetables. This can help keep your blood sugar steady.
2. Control portion sizes: Eating smaller, more frequent meals can prevent large spikes in blood sugar. Use measuring cups or a food scale if necessary to help with portion control.
3. Monitor carbohydrates: Keep track of the carbohydrates in your meals. Understanding how carbs affect your blood sugar can help you make better food choices.
4. Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day. Proper hydration helps your kidneys to flush out excess sugar through urine.
5. Regular physical activity: Exercise can improve insulin sensitivity and help regulate blood sugar levels. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise each week.
6. Get enough sleep: Aiming for 7-9 hours of sleep per night can help your body regulate insulin and maintain stable blood sugar levels.
7. Manage stress: Stress can cause blood sugar to spike. Practicing relaxation techniques like meditation or yoga can help manage stress effectively.
By following these tips and making small, sustainable changes to your lifestyle, you can maintain more stable blood sugar levels and improve your overall health.
Debunking common myths about blood sugar

Many people have misconceptions about blood sugar and its management, especially regarding type 2 diabetes. Let’s address some of these common myths.
Myth 1: Only sugary foods affect blood sugar levels.
In reality, all carbohydrates, including bread, pasta, and fruits, can impact blood sugar. It’s important to consider the total carbohydrate intake rather than just sugar.
Myth 2: If you have diabetes, you can never eat sweets.
While moderation is key, people with diabetes can still enjoy sweets occasionally. It’s about balance and monitoring how these foods affect your blood sugar levels.
Myth 3: Exercise isn’t important for blood sugar control.
On the contrary, regular physical activity can improve insulin sensitivity and help lower blood sugar levels. Aim for at least 150 minutes of exercise each week.
Myth 4: Blood sugar only needs monitoring during meals.
Blood sugar levels can fluctuate throughout the day. Regular monitoring, including before and after meals and during exercise, helps in understanding these changes.
Myth 5: People with diabetes cannot eat carbohydrates.
Carbohydrates are a key source of energy. The focus should be on the type and amount of carbs consumed rather than eliminating them entirely.
Understanding the truth behind these myths can lead to better management of blood sugar levels and overall health. Always consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice.
Managing blood sugar levels: Key takeaways
Managing blood sugar levels is crucial for individuals with type 2 diabetes. By understanding the impact of diet, exercise, and stress on blood sugar, you can make informed choices.
Monitoring your blood sugar regularly and following medication guidelines can help you maintain control. Additionally, debunking common myths about blood sugar can empower you in your health journey.
With the right strategies in place—like eating a balanced diet, staying active, and managing stress—you can lead a healthier life and achieve better blood sugar control. Always connect with your healthcare provider for personalized advice and support.
