Managing type 2 diabetes mellitus involves understanding symptoms, recognizing risk factors, maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, and utilizing advancements in treatment like continuous glucose monitoring for better blood sugar control.
Diabetes type 2 diabetes mellitus is more than just a condition; it’s a lifestyle challenge many face today. Have you ever wondered how it can alter daily routines and health? Let’s dive into understanding it better.
What is diabetes type 2 diabetes mellitus?
Diabetes type 2 diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition that affects the way your body metabolizes sugar (glucose), which is an essential source of fuel for your body. Unlike type 1 diabetes, where the body produces little or no insulin, in type 2 diabetes, your body either resists the effects of insulin—or doesn’t produce enough insulin to maintain a normal glucose level.
This condition is often linked to obesity, leading an inactive lifestyle, or an unhealthy diet. Over time, high blood sugar levels can lead to serious health complications, such as heart disease, kidney damage, and vision loss.
Symptoms of Diabetes Type 2
Common symptoms include frequent urination, increased thirst, extreme hunger, fatigue, and blurred vision. Some individuals may not experience any noticeable symptoms, which is why regular testing is crucial.
Risk Factors
Several factors may increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. These include being overweight, having a sedentary lifestyle, being over the age of 45, having a family history of diabetes, or having conditions such as high blood pressure or low HDL cholesterol.
Importance of Early Detection
Early detection through routine screening can lead to better management and can reduce the risk of serious health issues associated with diabetes. If you suspect you may be at risk, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional.
Symptoms to look out for

Recognizing the symptoms of diabetes type 2 diabetes mellitus is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management. Many people may not realize they have diabetes until symptoms become significant.
Some of the common symptoms include:
- Frequent urination: You may notice an increase in bathroom visits, especially at night.
- Increased thirst: As you lose more fluids, you may feel more thirsty than usual.
- Extreme hunger: Despite eating, you may still feel very hungry due to the body’s inability to use glucose properly.
- Fatigue: Feeling tired or sluggish can be a sign that your body is struggling to process glucose.
- Blurred vision: High blood sugar can lead to fluid being pulled from the lenses of your eyes, affecting your ability to see clearly.
- Slow healing sores: Cuts and bruises may take longer to heal, indicating potential issues with blood circulation and healing.
If you experience one or more of these symptoms, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and testing.
Risk factors and causes
Understanding the risk factors and causes of diabetes type 2 diabetes mellitus is essential for prevention and early intervention. Here are some of the most significant factors that may contribute to the development of this condition.
Obesity
Being overweight is one of the primary risk factors for developing type 2 diabetes. Extra body fat, particularly around the abdomen, can affect how your body uses insulin.
Physical Inactivity
A sedentary lifestyle increases the risk of type 2 diabetes. Regular physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight and improves insulin sensitivity.
Genetics
Your family history plays a vital role. If parents or siblings have diabetes, your risk of developing the condition increases significantly.
Age
As you get older, your risk of type 2 diabetes increases. This is particularly true after age 45, but it can occur at a younger age if other risk factors are present.
High Blood Pressure and Cholesterol
Conditions such as high blood pressure and low HDL (good) cholesterol can elevate your risk for type 2 diabetes, contributing to cardiovascular disease as well.
Gestational Diabetes
If you had diabetes during pregnancy, you may be at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Being aware of these risk factors can help in taking proactive steps toward prevention and maintaining a healthier lifestyle.
Managing diabetes through diet
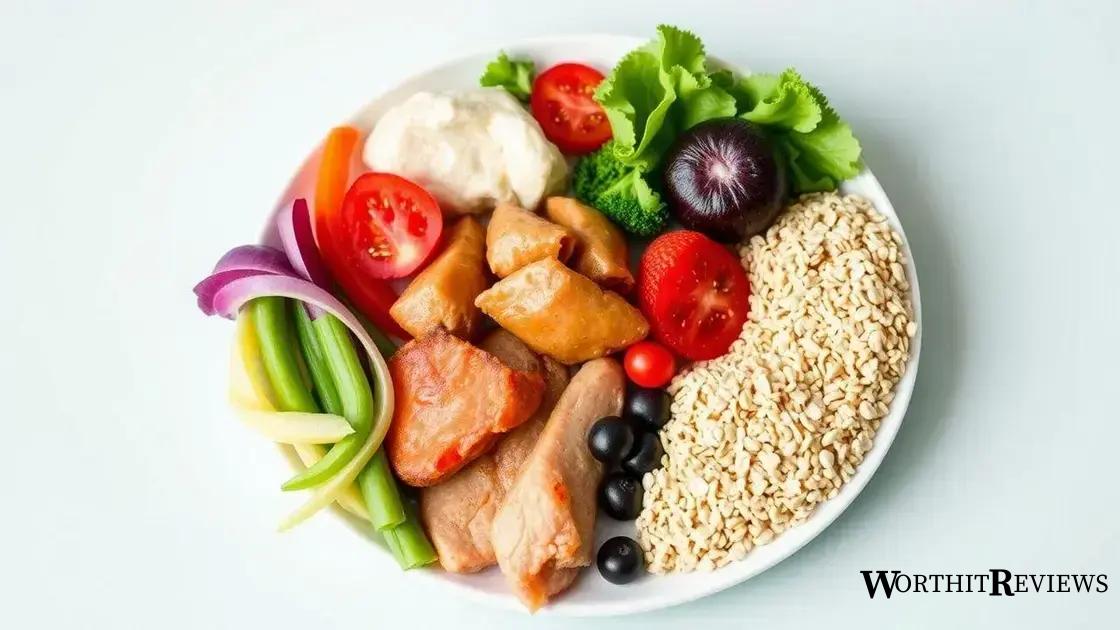

Managing diabetes type 2 diabetes mellitus effectively is significantly influenced by diet. A well-planned diet helps control blood sugar levels and promotes overall health. Here are key components to consider:
Understanding Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates have the most significant impact on blood sugar. Focus on whole grains, fruits, and vegetables while limiting refined carbs like white bread and sugary foods.
Choosing Healthy Fats
Incorporate healthy fats into your meals. Foods such as avocados, nuts, and olive oil can be beneficial. They help maintain heart health and support overall nutrition.
Balancing Protein Intake
Protein is essential for maintaining muscle mass. Include sources like lean meats, fish, legumes, and plant-based proteins. This helps in sustaining energy levels and preventing hunger spikes.
Portion Control
Watch portion sizes to avoid overeating. Using smaller plates and measuring food can help control portions and maintain balanced meals.
Regular Meal Timing
A consistent meal schedule helps keep blood sugar levels stable. Try to eat at similar times each day and avoid skipping meals.
Hydration
Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water. Avoid sugary drinks and limit consumption of alcohol, as they can impact your blood sugar levels.
Planning meals and being mindful of food choices are vital steps towards managing diabetes and leading a healthier life.
The role of exercise in diabetes management
Exercise plays a vital role in managing diabetes type 2 diabetes mellitus. Regular physical activity can help control blood sugar levels, reduce the risk of complications, and improve overall health.
Improving Insulin Sensitivity
Engaging in physical activity makes your body more sensitive to insulin, meaning your cells can use available sugar in the bloodstream more effectively. This helps lower blood sugar levels and keeps them in a healthier range.
Weight Management
Along with a balanced diet, exercise is essential for weight control. Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the risk of obesity-related complications associated with diabetes.
Types of Beneficial Exercises
Incorporating a mix of aerobic and strength-training exercises is beneficial. Walking, cycling, swimming, and resistance training can improve heart health and muscle strength.
Recommended Exercise Routine
For optimal benefits, aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity each week, along with strength training at least two days a week. Small activities, like taking the stairs or walking during breaks, also contribute positively.
Monitoring Blood Sugar
It’s important to monitor your blood sugar levels before and after exercise, especially when trying new activities. This helps understand how your body reacts and allows for adjustments in food intake or medication as needed.
Overall, a consistent exercise routine can dramatically enhance the quality of life for those managing diabetes and offer lasting health benefits.
New advancements in treatment and care
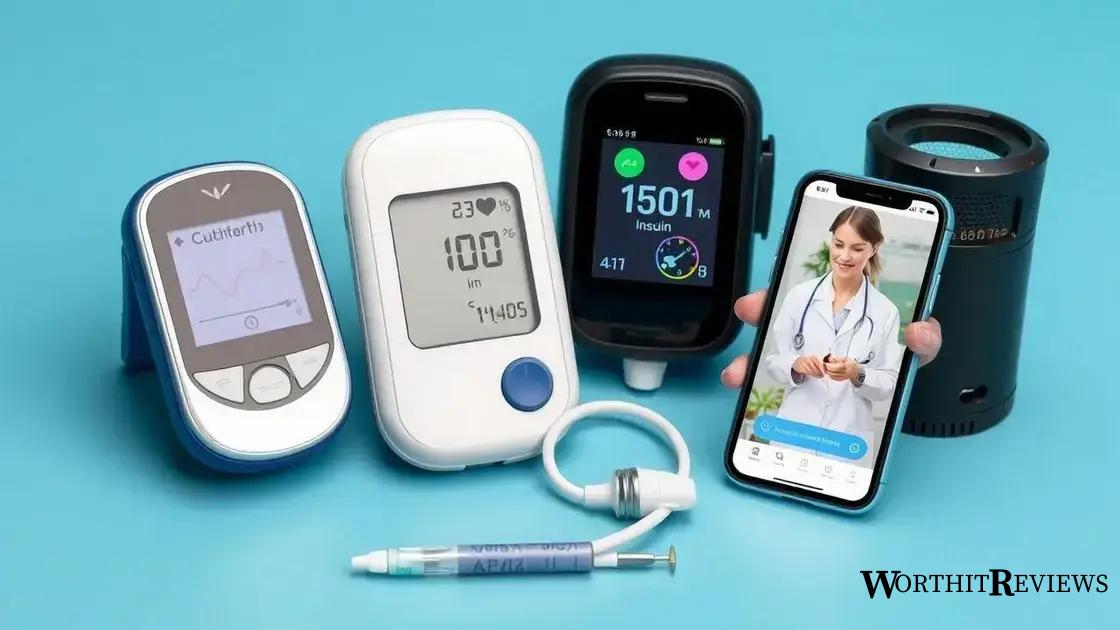
Recent advancements in the treatment and care of diabetes type 2 diabetes mellitus are making a significant impact on how individuals manage their condition. These innovations aim to improve blood sugar control and enhance the quality of life.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)
One of the most exciting advancements is the use of continuous glucose monitoring systems. These devices allow for real-time tracking of blood sugar levels, reducing the need for frequent finger-prick testing and providing valuable data for better management.
Insulin Pumps
Insulin pumps have also evolved, offering more precise delivery of insulin. Newer models can adjust insulin delivery based on blood sugar readings, enabling better glucose control with less effort from the patient.
Smart Insulin Patches
Innovative smart insulin patches are emerging, which automatically deliver insulin in response to blood sugar levels. These patches simplify management for those who have difficulty with traditional methods.
Medications
New classes of oral medications and injectables are improving blood sugar management. For instance, GLP-1 receptor agonists not only lower blood sugar but can also promote weight loss, addressing obesity, a common risk factor for diabetes.
Telehealth Services
Telehealth has become more accessible, allowing patients to consult healthcare providers via video calls and mobile apps. This enhances patient education, medication management, and overall support, especially for those in remote areas.
By staying informed about these advancements, individuals with diabetes can work closely with healthcare professionals to tailor their treatment plans and optimize their health outcomes.
In conclusion, managing diabetes type 2 diabetes mellitus is achievable
By understanding the symptoms, risk factors, and the essential role of diet and exercise, individuals can better control their health.
Advancements in treatment and care, such as continuous glucose monitoring and new medications, offer exciting opportunities for improved management.
Staying informed and proactive in your care can lead to better health outcomes and an overall improved quality of life.
With the right tools and support, it’s possible to thrive while managing diabetes.
