Managing blood sugar effectively involves monitoring levels regularly, maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in consistent physical activity, and understanding how stress impacts glucose levels.
Sugar blood sugar levels impact your daily life more than you might think. Have you ever wondered how simple changes can make a big difference? Let’s explore ways to manage your levels naturally.
Understanding sugar blood sugar levels
Understanding sugar blood sugar levels is essential for maintaining overall health. Blood sugar, or glucose, is crucial for energy, but too much of it can lead to serious health issues.
Blood sugar levels fluctuate throughout the day, influenced by what we eat, how active we are, and even our stress levels. Normal blood sugar levels typically range from 70 to 130 mg/dL when fasting and less than 180 mg/dL after meals.
Why Monitoring Blood Sugar is Important
Regular monitoring helps to prevent both high blood sugar (hyperglycemia) and low blood sugar (hypoglycemia). Each of these conditions has distinct symptoms and may lead to complications if not managed properly.
Factors Impacting Blood Sugar Levels
Several factors can affect sugar blood sugar levels, including:
- Diet: Foods high in carbohydrates, especially simple sugars, can cause rapid spikes in blood glucose levels.
- Activity Level: Regular physical activity helps lower blood sugar levels by improving insulin sensitivity.
- Medications: Some medications, especially those used to manage diabetes, directly impact blood sugar levels.
- Stress: Emotional or physical stress can lead to increased blood sugar levels due to hormone fluctuations.
Understanding your body’s response to these factors is essential for effective management of blood sugar levels.
Factors affecting blood sugar levels
Several factors play a critical role in determining blood sugar levels. Understanding these factors is vital for effective management.
Diet and Nutrition
The foods you eat have a direct impact on your blood glucose levels. Foods high in carbohydrates, especially simple sugars, can lead to quick spikes. Fiber-rich foods can help regulate these levels by slowing glucose absorption.
Physical Activity
Regular exercise is essential for controlling blood sugar. Physical activity helps your body use insulin more efficiently, which can lower blood sugar levels. Even a short walk can make a difference.
Stress Levels
Emotional and physical stress releases hormones like cortisol, which can raise blood sugar levels. Finding ways to manage stress through relaxation techniques or hobbies can help keep your levels steady.
Medications
Some medications can influence blood sugar levels. For instance, certain diabetes medications help lower blood sugar, while others may cause it to rise. It’s essential to consult with your healthcare provider about your medications and their effects.
Sleep Quality
Sleep deprivation or poor quality sleep can negatively impact blood sugar control. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep to help maintain healthy blood sugar levels.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations, such as during menstrual cycles or menopause, can also influence blood sugar. Women may experience changes in their blood sugar levels due to these hormonal shifts.
Natural methods to stabilize blood sugar
Stabilizing blood sugar naturally is essential for overall health. There are several methods you can incorporate into your daily routine.
Balanced Diet
Eating a well-balanced diet is key. Focus on whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. These foods help maintain steady glucose levels. Avoid processed foods and sugary snacks that can cause spikes.
Regular Exercise
Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking, cycling, or swimming, can improve your body’s insulin sensitivity. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week to help keep your blood sugar level in check.
Stay Hydrated
Drinking enough water is important for managing blood sugar. Staying hydrated helps your kidneys flush out excess sugar through urine. Aim to drink at least eight 8-ounce glasses of water each day.
Mindful Eating
Practice mindful eating by paying attention to your hunger and fullness cues. Avoid distractions during meals to help prevent overeating and promote better digestion, which aids in blood sugar management.
Limit Stress
High stress levels can affect your hormones and lead to elevated blood sugar levels. Incorporate stress-reducing techniques, such as mindfulness, yoga, or deep breathing exercises, into your daily routine.
Get Enough Sleep
Quality sleep plays a significant role in maintaining balanced blood sugar levels. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep each night, as poor sleep can negatively impact insulin sensitivity.
Common myths about sugar and blood sugar
There are many myths surrounding sugar and its effect on blood sugar levels. Understanding the truth can help in better management.
Myth 1: Eating sugar causes diabetes
Many believe that consuming sugar directly leads to diabetes. However, diabetes is more about insulin resistance and genetic factors than just sugar intake. A balanced diet is key.
Myth 2: All sugar is bad
Not all sugars are created equal. Natural sugars found in fruits and dairy come with beneficial nutrients and fiber. It’s added sugars in processed foods that can be harmful.
Myth 3: You can’t eat carbs if you have high blood sugar
Carbohydrates are a vital source of energy. The focus should be on the type and amount of carbs consumed. Complex carbohydrates, like whole grains, are better options than simple sugars.
Myth 4: You can’t manage blood sugar levels naturally
Many people think blood sugar management requires medication. In reality, lifestyle changes like diet, exercise, and sleep can significantly improve blood sugar control.
Myth 5: Artificial sweeteners are a safe alternative
While artificial sweeteners may seem like a better option, some studies suggest they can impact metabolism and increase cravings. Moderation is essential.
Myth 6: Eating more frequently keeps blood sugar stable
Some individuals think constant snacking helps maintain steady blood sugar. However, eating too much can lead to fluctuations. Focus on balanced meals instead.
Importance of diet in blood sugar control
The role of diet in controlling blood sugar is critical. What you eat directly impacts your glucose levels and overall health.
Choosing the Right Foods
Opt for whole, unprocessed foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. These foods provide essential nutrients and help stabilize blood sugar levels.
Carbohydrate Management
Managing carbohydrate intake is crucial. Focus on complex carbohydrates like brown rice and oats, which digest slowly, leading to gradual increases in blood sugar.
Portion Control
Being mindful of portion sizes helps prevent spikes in blood sugar. Use measuring cups or your plate’s sections to guide appropriate serving sizes.
Regular Meal Timing
Eating at regular intervals can help maintain consistent blood sugar levels. Aim for three balanced meals and healthy snacks throughout the day to avoid extreme fluctuations.
Incorporating Fiber
Fiber plays an essential role in blood sugar control. It slows the absorption of sugar, helping to keep levels steady. Foods high in fiber include beans, lentils, fruits, and vegetables.
Limiting Sugars and Refined Carbs
Avoiding added sugars and refined carbohydrates, like white bread and pastries, is key. These can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar and should be limited.
Monitoring your blood sugar effectively
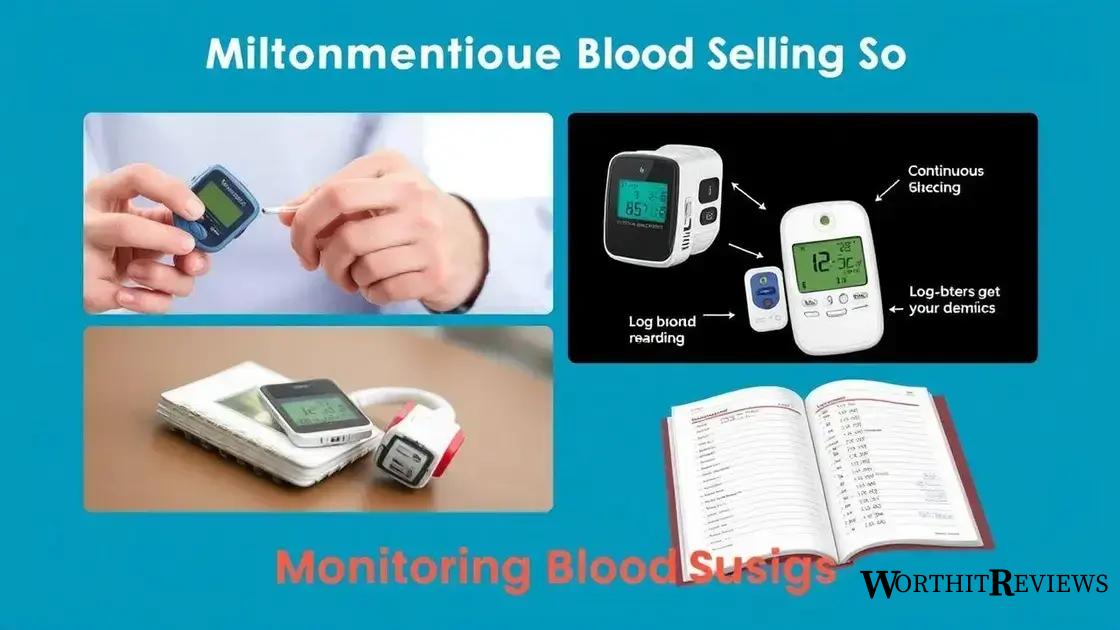
Effectively monitoring your blood sugar is essential for managing your health. Regular checks can help you understand how your body responds to food, exercise, and stress.
Understanding Different Methods
There are several ways to monitor blood sugar levels. The most common method is using a glucometer, a device that measures your blood glucose. Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) are another option, providing real-time data throughout the day.
When to Check Your Levels
To get accurate readings, it’s crucial to know when to test your blood sugar. Check your levels before meals, two hours after meals, and at bedtime. This will help you see how different foods affect your levels.
Keeping a Log
Recording your readings in a logbook or app can help you spot patterns over time. Include details such as your food intake, physical activity, and stress levels, as these can all influence blood sugar.
Understanding Your Target Range
Each person may have different target blood sugar ranges. General guidelines suggest fasting levels should be between 70-130 mg/dL and under 180 mg/dL after meals. Always talk to your healthcare provider about your specific targets.
Responding to High and Low Levels
If your blood sugar is too high, consider drinking water and engaging in physical activity. For lows, consume fast-acting carbohydrates, like fruit juice or glucose tablets, to quickly raise your levels.
Consulting with Healthcare Providers
Regular check-ins with your healthcare provider are crucial for personalized advice. They can help you adjust your plan based on your monitoring results and overall health.
In summary, managing your blood sugar is essential for good health
By understanding how various factors affect your levels, you can make informed choices. A balanced diet, regular exercise, and consistent monitoring play key roles in blood sugar management.
Knowing the myths surrounding sugar can help you make better food choices. Additionally, staying connected with healthcare professionals ensures that you’re on the right track.
With these tools and strategies, you can take control of your blood sugar and lead a healthier life.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions about Blood Sugar Management
What is a healthy blood sugar level?
A healthy blood sugar level is generally between 70-130 mg/dL when fasting and under 180 mg/dL after meals.
How often should I monitor my blood sugar?
It’s recommended to check your blood sugar before meals, two hours after meals, and at bedtime to understand how different factors affect your levels.
Can I manage blood sugar levels without medication?
Yes, many people can manage their blood sugar through diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes without medication.
What foods should I avoid to maintain healthy blood sugar?
Avoid foods high in added sugars and refined carbohydrates, such as sugary snacks, white bread, and sugary drinks.
How does stress affect blood sugar levels?
Stress can lead to hormonal changes that may raise blood sugar levels, making stress management techniques important for overall control.
What is the role of fiber in blood sugar control?
Fiber helps slow the absorption of sugar, leading to more stable blood sugar levels and reducing spikes after meals.
