Managing sugar levels in type 2 diabetes involves a balanced diet, regular exercise, and consistent monitoring of blood glucose levels to ensure better health outcomes.
The sugar level of type 2 diabetes is a key factor in managing overall health. Have you ever wondered how it affects your daily life or what steps you can take to keep it in check? This article will delve into essential insights and practical tips for maintaining a healthy sugar level.
Understanding type 2 diabetes and sugar levels
Understanding type 2 diabetes and its link to sugar levels is crucial for effective management. Type 2 diabetes occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough insulin, leading to high blood sugar levels. Monitoring these levels helps avoid complications and promotes overall health.
What Are Normal Sugar Levels?
Normal blood sugar levels usually fall between 70 to 130 mg/dL before meals and should be less than 180 mg/dL two hours after eating. Keeping sugar levels in this range is essential for preventing health issues.
Factors Affecting Sugar Levels
Several factors can influence blood sugar levels in individuals with type 2 diabetes. These include diet, physical activity, stress, and medications. For instance, consuming carbohydrates raises sugar levels, while regular exercise can help lower them.
Identifying High and Low Sugar Levels
Recognizing the signs of high blood sugar, such as increased thirst and frequent urination, is vital. On the other hand, low blood sugar can manifest as shakiness, confusion, and sweating. Being aware of these symptoms allows for timely intervention.
The Importance of Regular Monitoring
Regularly checking your sugar levels is critical in managing type 2 diabetes. Frequent monitoring helps you understand how food, activity, and stress impact your blood sugar, enabling better decision-making regarding your health.
Symptoms of high and low sugar levels
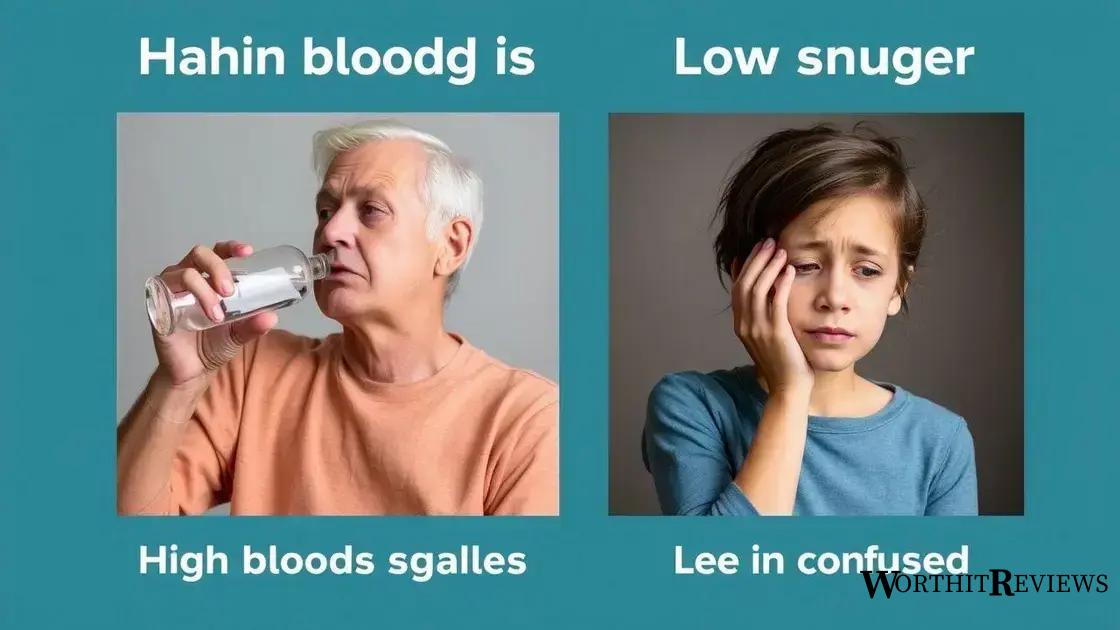
Recognizing the symptoms of high and low sugar levels is essential for managing type 2 diabetes effectively. Understanding these signs can help you take appropriate action quickly.
Symptoms of High Sugar Levels
When blood sugar levels are too high, also known as hyperglycemia, the body may exhibit several signs. Common symptoms include:
- Increased thirst
- Frequent urination
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing cuts or bruises
High sugar levels can lead to serious complications if not addressed promptly.
Symptoms of Low Sugar Levels
On the flip side, low blood sugar, or hypoglycemia, can also be dangerous. Symptoms may include:
- Shakiness
- Confusion
- Sweating
- Rapid heartbeat
- Feeling lightheaded or dizzy
Low sugar levels require immediate attention, such as consuming a fast-acting carbohydrate.
Importance of Monitoring Symptoms
Being aware of these symptoms helps you respond quickly. Regular monitoring of your blood sugar levels can help you identify patterns and avoid episodes of hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia.
How diet impacts sugar levels in type 2 diabetes
Diet plays a vital role in managing type 2 diabetes and regulating sugar levels. Choosing the right foods can help maintain stable blood sugar and prevent complications.
Understanding Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates have the most significant impact on blood sugar levels. They break down into glucose during digestion, leading to increased sugar levels. It’s essential to choose complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, over simple sugars found in sweets and processed foods.
The Glycemic Index
The glycemic index (GI) measures how quickly foods raise blood sugar levels. Foods with a high GI, like white bread and sugary snacks, can cause rapid spikes in sugar levels. In contrast, low-GI foods, such as legumes and non-starchy vegetables, help maintain stable levels.
Portion Control
Another crucial factor is portion control. Eating large portions can lead to excess calorie intake and higher blood sugar levels. Balancing your plate with appropriate portion sizes of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats can support better management of diabetes.
Including Fiber
A diet high in fiber can aid in regulating blood sugar levels. Fiber slows down digestion, which helps prevent spikes in blood sugar. Aim to include fiber-rich foods, such as whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes, in your meals.
Staying Hydrated
Staying properly hydrated is essential for overall health and can help maintain sugar levels. Water is the best choice, while sugary beverages can lead to increased blood sugar. Aim to drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated.
The role of exercise in regulating sugar levels

Exercise plays a crucial role in managing type 2 diabetes and regulating sugar levels. Regular physical activity can significantly impact overall health and blood sugar control.
How Exercise Affects Blood Sugar
When you engage in physical activity, your muscles use glucose for energy. This process helps lower blood sugar levels. Regular exercise improves insulin sensitivity, meaning your body can use insulin more effectively, leading to better sugar control.
Types of Beneficial Exercises
Incorporating different types of exercise into your routine is important:
- Aerobic exercises: Activities like walking, jogging, cycling, and swimming can elevate your heart rate and improve cardiovascular health.
- Strength training: Lifting weights or bodyweight exercises help build muscle mass, which can further enhance glucose uptake by the muscles.
- Flexibility and balance exercises: Practices like yoga and tai chi can improve overall mobility and reduce the risk of injuries.
Setting Exercise Goals
Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity each week. Break it down into manageable sessions, such as 30 minutes a day, five days a week. Set realistic goals that can help you stay consistent and motivated.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
It’s essential to monitor your blood sugar levels before and after exercising. This helps you understand how your body responds to different activities. Be aware that physical activity can sometimes cause both increases and decreases in blood sugar, so adjustments may be necessary.
Consulting Your Healthcare Provider
Before starting any exercise program, consult with your healthcare provider. They can guide you on safe practices based on your individual health needs and provide recommendations tailored to your personal situation.
Monitoring your sugar levels effectively
Monitoring your sugar levels is crucial for managing type 2 diabetes effectively. Keeping track of blood glucose helps you make informed decisions about your diet, exercise, and medication.
Benefits of Regular Monitoring
Regularly checking your sugar levels allows you to understand how your body responds to different foods and activities. This knowledge can help you avoid spikes or drops in blood sugar, leading to better overall health.
When to Check Blood Sugar
It’s important to know when to test your blood sugar. Common times include:
- Before meals
- 1-2 hours after meals
- Before and after exercising
- When feeling symptoms of high or low blood sugar
Choosing the Right Monitoring Method
You can monitor your sugar levels through various methods:
- Fingerstick tests: Using a glucose meter with small blood samples is the most common method.
- Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs): These devices provide real-time glucose readings throughout the day without finger pricks.
Understanding Your Readings
Normal blood sugar readings should be:
- 70 to 130 mg/dL before meals
- Less than 180 mg/dL 1-2 hours after meals
Consult your healthcare provider for target levels specific to your situation.
Keeping a Log
Keeping a log of your blood sugar readings, diet, and activities can help identify patterns and triggers. This information can be valuable in discussions with your healthcare team about your diabetes management plan.
Common misconceptions about sugar and diabetes

Understanding common misconceptions about sugar and diabetes is crucial for effective management of the condition. Misinformation can lead to poor health choices and unneeded anxiety.
Myth 1: Eating Sugar Causes Diabetes
Many believe that eating sugar directly causes diabetes. While a high-sugar diet can contribute to weight gain and increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, sugar alone does not cause the disease.
Myth 2: People with Diabetes Can’t Eat Sugar
Another common belief is that individuals with diabetes must completely avoid sugar. In reality, people with diabetes can include sugar in their diets in moderation. The key is to balance sugar intake with overall nutrition and portion control.
Myth 3: All Carbohydrates Are Bad
Some think that all carbohydrates should be avoided. However, carbohydrates are a necessary part of a balanced diet. It’s important to focus on complex carbohydrates like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables rather than simple sugars, which can spike blood sugar levels.
Myth 4: Diabetes Is Only a Disease of Older Adults
Diabetes affects people of all ages. While type 2 diabetes is more common in adults, children and adolescents can also develop the condition, especially with rising obesity rates.
Myth 5: Once You Have Diabetes, You Can’t Change It
Some believe that diabetes is irreversible. However, with lifestyle changes such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, and weight management, it is possible to improve blood sugar control and even achieve remission for some.
Advice from experts: managing sugar levels
Managing sugar levels effectively is crucial for those with type 2 diabetes. Expert advice can provide valuable insights for maintaining healthy blood glucose levels.
Follow a Balanced Diet
Experts recommend focusing on a balanced diet that includes whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Incorporate plenty of vegetables and limit processed foods high in sugar. Understanding portion sizes can help prevent spikes in blood sugar.
Stay Hydrated
Drinking enough water is essential for overall health. Staying hydrated helps your kidneys flush out excess sugar through urine. Experts suggest aiming for at least 8 cups of water a day, more if you’re active.
Regular Physical Activity
Engaging in regular exercise improves insulin sensitivity and helps regulate blood sugar levels. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity each week. Include a mix of cardiovascular, strength training, and flexibility exercises.
Monitor Your Blood Sugar
Regular monitoring of your blood sugar levels helps you understand how different foods and activities affect your glucose. Track your levels before and after meals to identify patterns and make informed decisions about your management strategy.
Manage Stress
Stress can cause fluctuations in blood sugar levels. Experts advise adopting stress-reduction techniques, such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises. Finding time for relaxation can positively impact your overall well-being.
Consult Healthcare Professionals
Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are essential. They can offer personalized advice, adjust medications, and provide ongoing support to help you effectively manage your diabetes.
Tips for creating a sustainable diet plan

Creating a sustainable diet plan is essential for managing type 2 diabetes and maintaining overall health. The following tips can help you design a plan that supports your health goals while being realistic and enjoyable.
Focus on Whole Foods
Base your diet on whole foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. These foods provide essential nutrients and help regulate blood sugar levels.
Plan Your Meals
Planning your meals in advance can help you make healthier choices. Create a weekly menu that includes balanced meals and snacks. This approach makes it easier to avoid impulse eating and can save time during busy days.
Control Portion Sizes
Be mindful of portion sizes to prevent overeating. Use measuring cups or a scale to help gauge portions and try to fill half your plate with vegetables. Understanding proper serving sizes can aid in blood sugar management.
Incorporate Variety
Avoid monotony by incorporating a variety of foods into your diet. Experiment with new fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to keep meals interesting and nutritionally balanced. This also ensures you get a wide range of nutrients.
Stay Hydrated
Water is the best choice for hydration. Aim to drink at least 8 cups of water a day. Staying hydrated can help control hunger and support overall health, making it easier to stick to your diet plan.
Limit Processed Foods and Sugars
Reduce your intake of processed foods, sugary snacks, and beverages. These items can lead to blood sugar spikes and do not provide lasting energy. Opt for healthier snack alternatives, such as nuts, fruits, and yogurt.
Seek Professional Guidance
Consider working with a registered dietitian or nutritionist to create a personalized diet plan. They can provide tailored advice based on your specific health needs and preferences, helping you achieve your goals.
Managing sugar levels and diabetes effectively
Managing sugar levels is essential for those with type 2 diabetes. By following a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, and monitoring your blood sugar, you can achieve better health. Understanding common misconceptions about sugar and diabetes can also help you make informed decisions.
Seeking expert advice and creating a sustainable diet plan tailored to your needs will support your management efforts. Remember, it’s about making consistent, healthy choices that work for your lifestyle.
With the right strategies in place, you can live a full and healthy life while managing your diabetes effectively.
